LogisticRegression¶
-
class
getml.predictors.LogisticRegression(learning_rate=0.9, reg_lambda=1e-10)¶ Bases:
getml.predictors._PredictorSimple predictor for classification problems.
Learns a simple linear relationship using the sigmoid function:
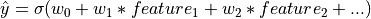
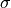 denotes the sigmoid function:
denotes the sigmoid function: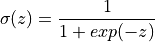
The weights are optimized by minimizing the cross entropy loss of the predictions
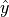 w.r.t. the targets
w.r.t. the targets 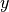 .
.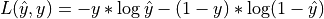
Logistic regressions are always trained numerically.
If you decide to pass categorical features to the
LogisticRegression, it will be trained using the Broyden-Fletcher-Goldfarb-Shannon (BFGS) algorithm. Otherwise, it will be trained using adaptive moments (Adam). BFGS is more accurate, but less scalable than Adam.- Parameters
learning_rate (float, optional) – The learning rate used for the Adaptive Moments algorithm (only relevant when categorical features are included). Range: (0,
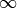 ]
]reg_lambda (float, optional) – L2 regularization parameter. Range: [0,
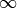 ]
]
- Raises
TypeError – If any of the input arguments does not match its expected type.
Note
This class will be trained using the
fit()method and used for prediction using thepredict()method of eitherMultirelModelorRelboostModel.Methods Summary
validate()Checks both the types and the values of all instance variables and raises an exception if something is off.
Methods Documentation
-
validate()¶ Checks both the types and the values of all instance variables and raises an exception if something is off.
Examples
l = getml.predictors.LogisticRegression() l.learning_rate = 20 l.validate()
- Raises
KeyError – If an unsupported instance variable is encountered.
TypeError – If any instance variable is of wrong type.
ValueError – If any instance variable does not match its possible choices (string) or is out of the expected bounds (numerical).
Note
This method is called at end of the __init__ constructor and every time before the predictor - or a class holding it as an instance variable - is send to the getML engine.